Linting Python in Visual Studio Code
Linting highlights syntactical and stylistic problems in your Python source code, which often helps you identify and correct subtle programming errors or unconventional coding practices that can lead to errors. For example, linting detects use of an uninitialized or undefined variable, calls to undefined functions, missing parentheses, and even more subtle issues such as attempting to redefine built-in types or functions. Linting is distinct from Formatting because linting analyzes how the code runs and detects errors whereas formatting only restructures how code appears.
Note: Stylistic and syntactical code detection is enabled by the Language Server. To enable third-party linters for additional problem detection, you can enable them by using the Python: Select Linter command and selecting the appropriate linter.
Choose a linter
Install the linting tool of your choice from the VS Code Marketplace.
Microsoft publishes the following linting extensions:
Linting extensions offered by the community:
| Linter | Extension |
|---|---|
| Ruff | https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=charliermarsh.ruff |
| mypy | https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=matangover.mypy |
Note: If you don't find your preferred linter in the table above or in the Marketplace, you can add support for it via an extension. You can use the Python Extension Template to integrate new Python tools into VS Code.
General Settings
| Setting | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| args | [] |
Arguments to be passed to the linter. Note: The officially supported linters run on individual open files. Make sure your configuration applies in that scenario. |
| importStrategy | useBundled |
When set to useBundled, the extension uses the version of the tool that it ships with. When set to fromEnvironment, it attempts to load from your selected Python environment first, otherwise it falls back to the bundled version. |
Disable linting
Linters, if installed, are enabled by default. You can disable them by disabling the extension per workspace.
Run linting
Linting will automatically run when a Python file is opened or saved.
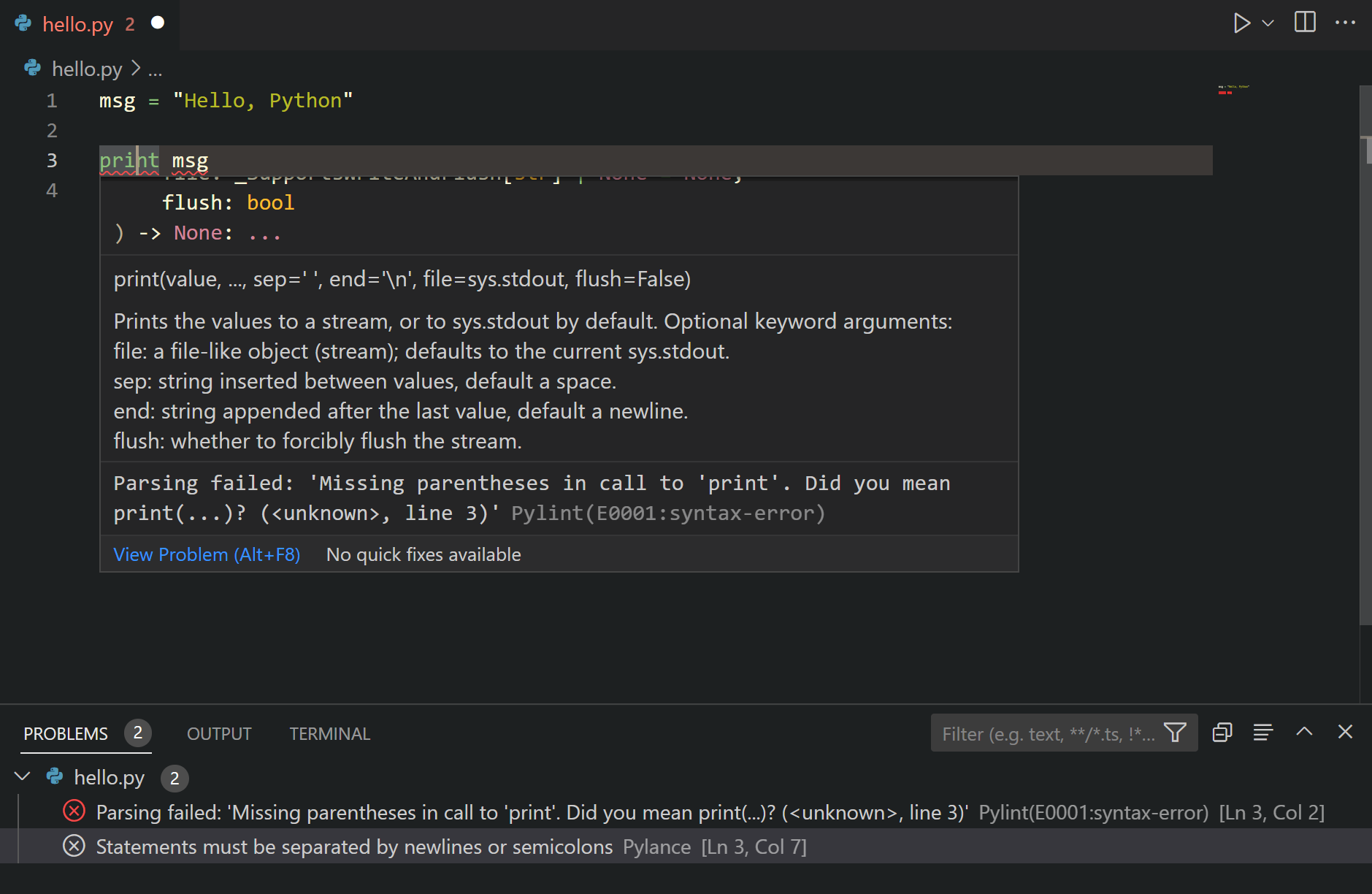
Errors and warnings are shown in the Problems panel (⇧⌘M (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+M)) for open files, and are also highlighted in the code editor. Hovering over an underlined issue displays the details:
Code Actions
Some linters may offer Code Actions that can help address reported problems. You can refer to the Feature Contributions section under your preferred linter extension to find out what Code Actions it offers.
Logging
Logs for linters are available in the Output panel (⇧⌘U (Windows Ctrl+Shift+U, Linux Ctrl+K Ctrl+H)) when you select <linter name> from the drop down menu.
You can change the log level for a linter extension by running the Developer: Set Log Level command from the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)). Select the extension from the Extension Logs group, and then select the desired log level.
Severity
Linters report issues with some predefined severity. This can be changed using severity setting for the linter. Refer to each linter extension's README for more details on the supported values and severity levels.
Troubleshooting linting
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No problems reported | No Python has been selected for your workspace. | Look at the logs for the linter you are using and check the path to the Python environment it's using. If there is no Python selected, run the Python: Select Interpreter command from the Command Palette and select an existing interpreter for your workspace. |
Next steps
- Debugging - Learn to debug Python both locally and remotely.
- Testing - Configure test environments and discover, run, and debug tests.
- Basic Editing - Learn about the powerful VS Code editor.
- Code Navigation - Move quickly through your source code.
- Python Extension Template - Create an extension to integrate your favorite linter into VS Code.